What is carbon farming?
According to the handbook of carbon farming by EU, the definition is as follows;
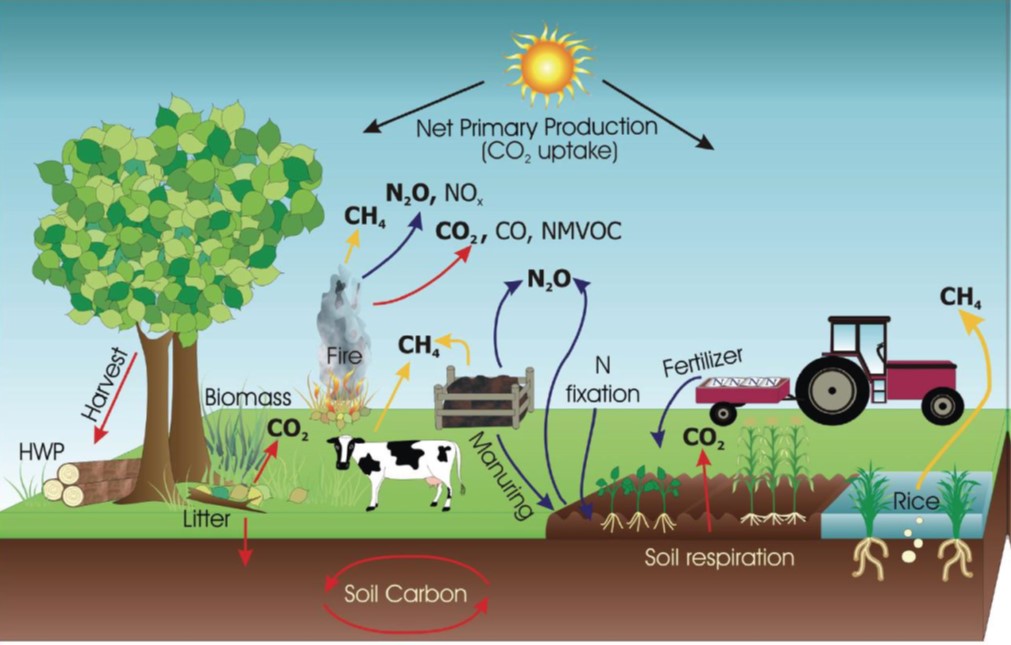
Carbon farming refers to the management of carbon pools, flows and GHG fluxes at farm level, with the purpose of mitigating climate change. This involves the management of both land and livestock, all pools of carbon in soils, materials and vegetation, plus fluxes of carbon dioxide (CO₂) and methane (CH4), as well as nitrous oxide (N2O) (which is included among relevant fluxes of GHGs in the agricultural sector by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) and therefore is considered part of carbon farming). This is illustrated in Figure 1.
Carbon farming is called regenerative farming. It adapts the same principles of natural farming.
Documentary video of carbon farming practice
To understand the actual practices, science evidence ,and benefits, please watch the following video made by NHK (The Japan Broadcasting Corporation)
Carbon Farming: A Climate Solution Under Our Feet – NHK WORLD PRIME (the link to the movie)
Technical Guidance Handbook
EU prepared the technical guidance handbook to practice this farming.
You can find the EU’s approach to carbon farming and technical guide on the following carbon farming page of the EU;
Carbon farming (Climate action age of EU)
Natural farming was scientifically verified to produce healthy foods with minimum inputs and mitigate climate change.
Recently we are facing a lack of agricultural inputs such as chemical fertilizers pesticides and imported grain for livestock.
In the age of sustainability, we should find a way to maximize outputs with minimal energy input.
This is the concept of “Dymaxion” which is a term coined by architect and inventor, Buckminster_Fuller.
Let’s start new businesses with this farming and support this innovative and revolutionary solution for climate change.

Hi, Mr Tsuboi!
How are you!
Hope you are fine!
In the context of carbon farming, Algeria is aiming for planting, over the next few years, as part of various reforestation programs.
Carbon sequestration can become a key instrument of global climate strategy if carbon capture sectors continue to innovate and grow.
Carbon sequestration technologies need to be developed and scaled up to make them commercially viable.
The biological pathway and in particular forests, generally considered to be important carbon sinks, will require significant changes in land use and management practices, such as afforestation/reforestation, changes in forest management or changes radicals in agricultural practices that improve carbon storage in the soil.
It is therefore important to focus on the direction of the net flux of carbon in biological systems, while emphasizing the role of carbon in restoring and augmenting our natural systems.
However, it is likely to be extremely costly to reduce anthropogenic emissions once they reach low levels.
While biological methods have significant potential for reducing atmospheric carbon, each of them raises concerns. It is therefore important to build expertise to discuss the potential of biological carbon sequestration, the need for policy incentives and pathways to achieve large-scale performance.
Finally, the economic aspect is a major obstacle to the deployment of many of these climate change mitigation measures, especially in the absence of a price for carbon.
Yours,
Nesrine charef.
Algeria.
Hi, Nesrine-san,
Thank you for your comment.
As you mentioned, biological or natural solutions are better than chemical or mechanical solutions,
especially for food. If we realize this fact, we can have solutions for the current problems about aliment and agriculture.